Lecture 11: Smooth Particle Hydrodynamics – Lecture + Hands-on
Institute for Physics and Astronomy, University of Potsdam
January 23, 2024
1 Lecture overview
Table of Contents 1/2
- 17.10. Introduction + numerical methods summary
- 24.10. Numerical methods of differential equations — lecture + hands-on
- 31.10. State holiday
- 07.11. Test particle approach — lecture
- 14.11. Test particle approach — lecture + hands-on
- 21.11. PIC method — lecture
- 28.11. PIC method — hands-on
Table of Contents 2/2
- 05.12. Fluid and MHD — lecture (online)
- 12.12. Fluid and MHD — hands-on given Xin-Yue Shi
- 19.12. Canceled
- 09.01. Radiative transfer — lecture + hands-on
- 16.01. HPC computing — lecture + hands-on**
- 23.01. Advanced — Smooth particle hydrodynamics method — lecture
- 30.01. Advanced — Hybrid, Gyrokinetics — lecture
- 06.02. Advanced — Vlasov and Linear Vlasov dispersion solvers — lecture
2 Introduction
2.1 Properties of SPH
- Lagrange methods
- Particles representing a part of plasma/fluid
- Mesh-less
2.2 Kernel function
- Kernel function describes a smooth quantity by weighting macro-particles
- Similar to PIC weighting/smooth function of macro-particles \[ f(\vec{x}) = \int_{\Omega} f(\vec{y}) W(\vec{x} - \vec{y}, h) d\vec{y} \]
- \(h\) is the smoothing length
- for \(h \rightarrow\) 0, \(W\) approach delta function
- for \(|\vec{r}| > K_{max} h\), we define \(W(\vec{r}) = 0\)
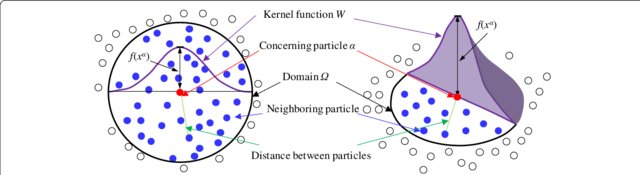
SPH kernel function (DOI).
2.3 Kernel function
- The field \(f\) is obtained by discretization into macro-particles
- Macro-particles have mass \(m_i\), density \(\rho_i\), and volume \(V_i = m_i / \rho_i\)
- In the most simple (fluid) case, each macro-particles has position \(\vec{i}\), velocity \(\vec{v}_i\)
- For a finite number of macro-particles, the kernel is expressed as \[ f(\vec{x}_i) = \sum_{j} V_j f(\vec{x}_j) W(\vec{x}_i - \vec{x}_j, h) \]
- For example, fluid density is \[ \rho(\vec{x}_i) = \sum_{j} m_j W(\vec{x}_i - \vec{x}_j, h). \]
3 Equations of motion
3.1 Equations of motion
- Using SPH approach to discretize fluid equations of motion
- In Lagrangian form \[ \frac{d \rho}{dt} = - \rho \nabla \cdot \vec{u} \] \[ \frac{d\vec{u}}{dt} = - \frac{1}{\rho} \nabla p + \nu \nabla^2 \vec{u} + \vec{g} \]
- \(p\) is the pressure
- \(\rho\) is the density
- \(\nu\) is the kinematic viscosity
- \(\vec{g}\) is the acceleration due to the external force
3.2 Weakly compressible fluid
- In weakly compressible fluid (not typical for astrophysics), equation of state is \[ p = \frac{c_0^2 \rho_0}{\gamma} \left[ \left( \frac{\rho}{\rho_0} \right)^\gamma - 1 \right] \]
- $= 7 $ is the adiabatic index
- \(\rho_0\) - reference density (to which we assume the perturbation
- \(c_0\) is the sound speed (for the reference density)
3.3 Discrete form of equations of motion
- Then, the equations of motion get form \[ \frac{d \rho_i}{dt} = \sum_j m_j (\vec{v}_i - \vec{v}_j) \cdot \nabla_i W_{i,j} \] \[ \frac{d\vec{u}_i}{dt} = \vec{a}_p + \vec{a}_{visc} + \vec{a}_{body} \] where \[ \vec{a}_p = - \sum_j m_j \left( \frac{p_i}{\rho_i^2} + \frac{p_j}{\rho_j^2} \right) \nabla_i W_{i,j} \] is the acceleration due to other particles.
- \(p_i\) is the pressure on \(i\)-th particle created by pressure \(p_j\) of \(j\)-th particle
- \(\nabla_i W_{i,j} = \frac{\partial W (\vec{x}_i - \vec{x}_j, h)}{\partial \vec{x}_i}\) is the gradient of the kernel function.
3.4 Discrete form of equations of motion
\[ \vec{a}_{visc} = \sum_j m_j \frac{4\nu}{(\rho_i + \rho_j)} \frac{\vec{r}_{i,j} \cdot \nabla_i W_{i,j}}{(|\vec{r}_{i,j}|^2 + \eta h^2)} \vec{u}_{i,j} \] is the acceleration due to viscous forces
\(\vec{r}_{i,j} = \vec{x}_i - \vec{x}_j\)
and \(\vec{a}_{body}\) is the acceleration due to external force.
Particle positions are obtained by \[ \frac{d\vec{x}_i}{dt} = \vec{u}_i \]
Some boundary conditions should be considered.
4 Numerical algorithms
4.1 Particle push — particle time integration
Typically, predictor-corrector scheme is used:
- \[ \vec{u}_i^{n + \frac{1}{2}} = \vec{u}_i^n + \frac{\Delta t}{2} \left( \frac{d \vec{u}_i}{dt} \right)^n, \]
- \[ \vec{x}_i^{n+1} = \vec{x}_i^n + \Delta t \vec{u}_i^{n + \frac{1}{2}}, \]
- \[ \vec{u}_i^{n+1} = \vec{u}_i^{n+\frac{1}{2}} + \frac{\Delta t}{2} \left( \frac{d \vec{u}_i}{dt} \right)^{n+1}. \]
CFL condition must be fulfilled \[ \Delta t < \frac{\Delta x}{c}. \]
Implicit schemes are not usual.
4.2 Search of nearest neighbor particles
- The methods would be extremely computational demanding if all particles interact with each other
- For motion of each particle, we need to know the neighboring particles that influence its motion
- These algorithms are known as ‘’nearest neighbor particles search’’ (NNPS)
- Used also in many other computational disciplines like computational chemistry, engineering, …
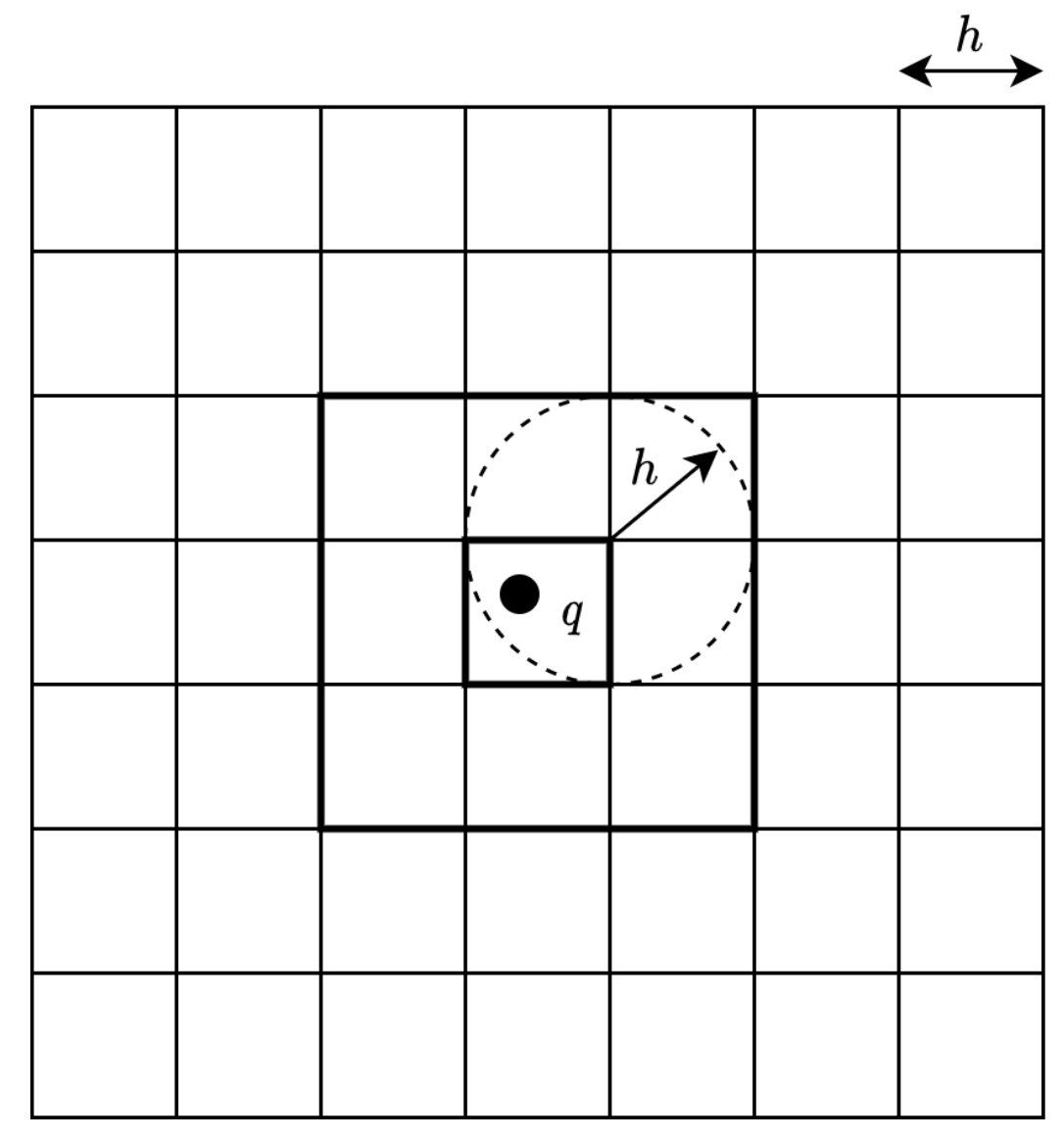
4.3 How it works:
- Particle are devided into cells of an uniform grid
- The grid size is the particle radius (for various particles radii, the largest must be used)
- Neighbors are always the particles in surrounding boxes
- Works well for constant particle radii
4.4 NNPS for variable radii
- When particles can change their radii, some cells contain only a few particles while other really many
- Various data structures were proposed to efficiently handle particle neighbors
- Options:
- Octree - Widely used; divide the 3D grid cell into 8 octants into subgrids untill the subgrid has less than specified number of particles; well for parallelization; manipulation with subgrids not so easy.
Octree algorithm DOI.
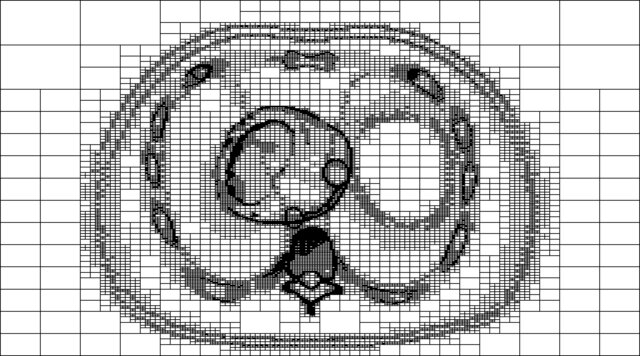
4.5 Linked list
- Mapping each cell to an ID which is mapped into a head array of particles-
- The head array stores the first particle of that cell
- There is second array that maps the next particle;
- Better cache performance, but needs to allocate large array.
Linked list (DOI)
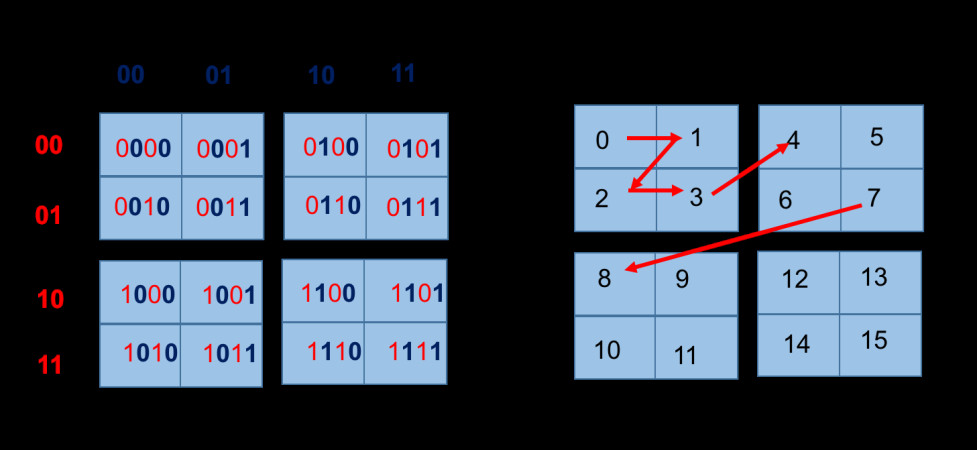
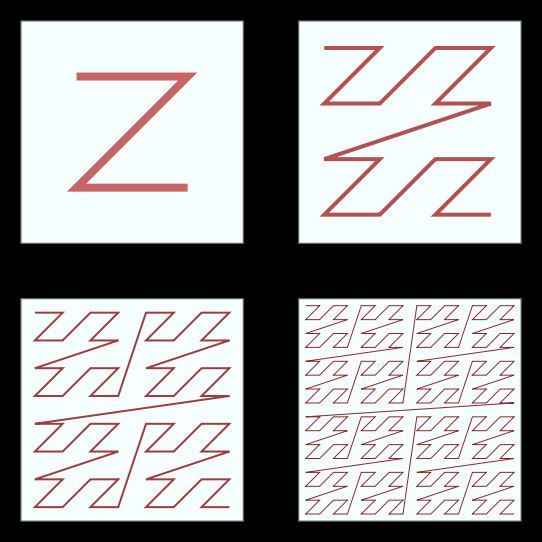
4.6 Z-Order Space Filling Curve
- Create a spatial order of surrounding particles;
- Sorting particles order based on their localization;
- This way close particles in space are close in the list.
5 SPH examples
5.1 Non-astrophysical examles of fluids
- Fluid examples
- Comparison of water and SPH fluid evolution
- Tutorial - Play close to time 43:50
- Some fun
5.2 Astrophysical examples
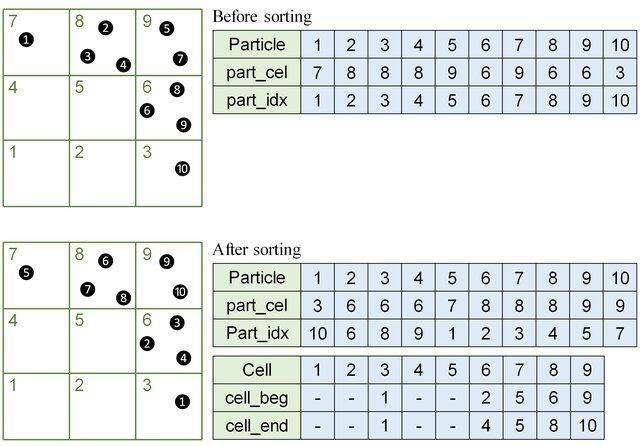
5.3 Simulations of Galaxies
Hopkins 2015 – Traditional SPH (TSPH), Modern SPH (PSPH), Mesh-less Finite Mass (MSM), and Mesh-less Finite Volume (MFV).
5.4 Star formation
5.5 Planet formation
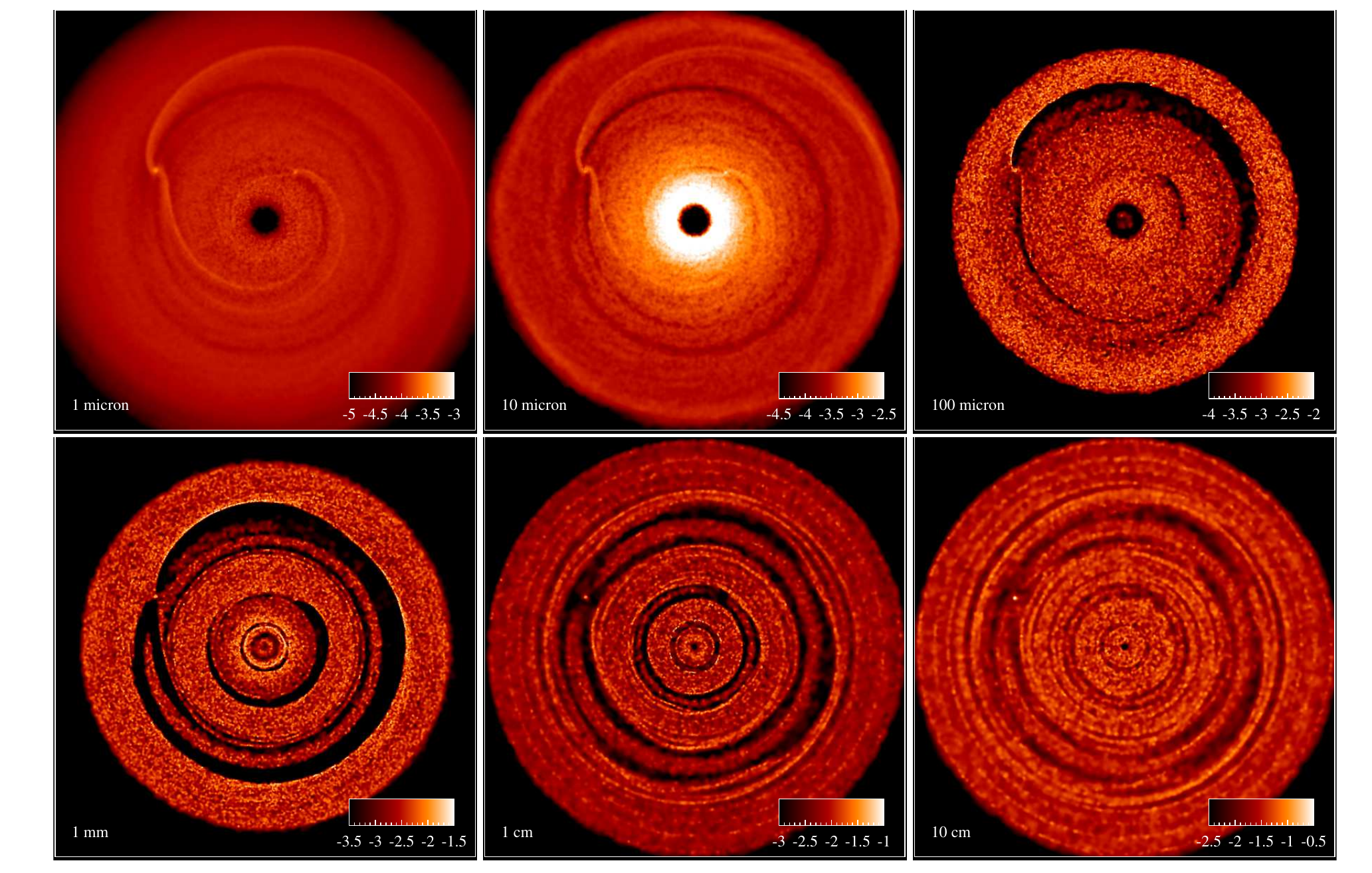
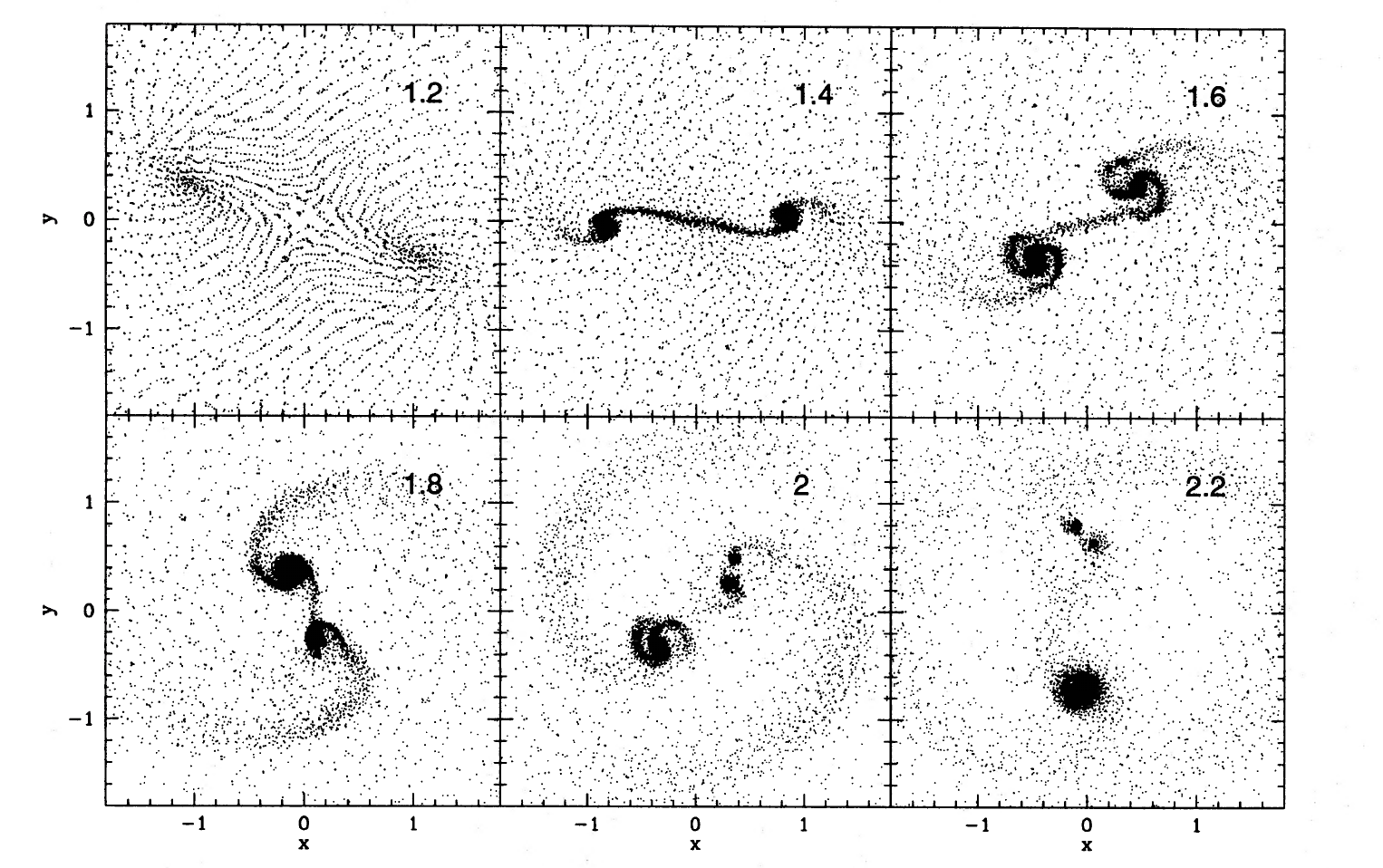
5.6 Moon formation
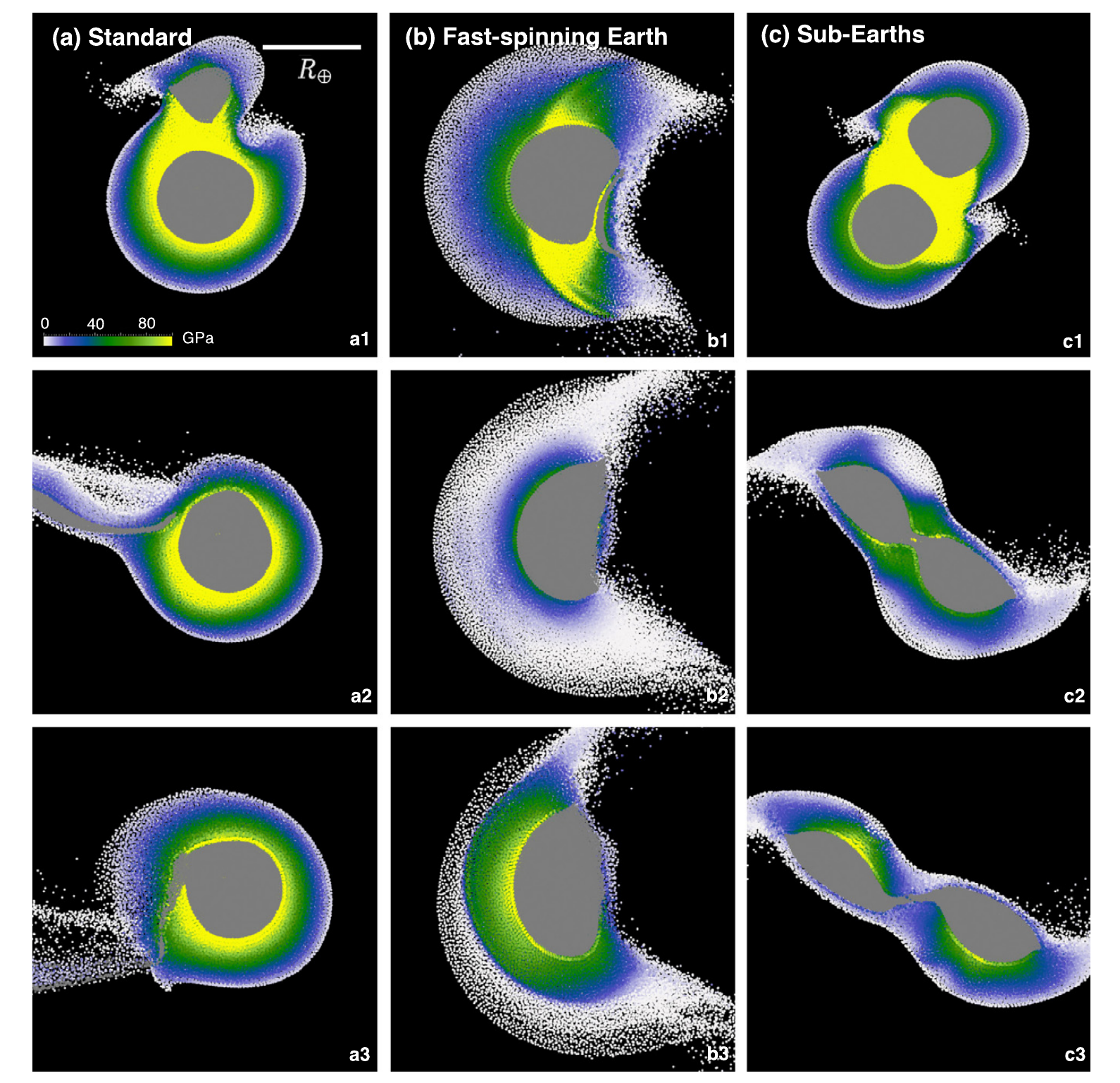
Nakajima and Stevenson (2015) (a) standard: a Mars-sized impactor hits the proto-Earth, (b) fast-spinning Earth: a small impactor hits a rapidly rotating proto-Earth, and (c) sub-Earths: two half Earth-sized planets collide.
6 Hands-on session
6.1 Hands-on session
Download the code
Run the code
Tasks:
- What quantities are plotted?
- Why the final curve is not the same as the theoretical prediction?
- How do you interpret the particle motion?
- Why the oscillation amplitudes decrease in time?
- How to decrease the oscillations of particles?